I’ve been starting to use twitter – mainly to supplement my research interests. I have zero confidence in facebook as a useful platform for anything remotely scientific or supportive of science, but twitter somehow seems different. The first twitter account I followed was @BeijingAir early this calendar year as reports of ridiculously bad air quality emerged yet again. I was quickly impressed by this informal but rigorous reporting of hourly (!) air quality relevant metrics such as particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations.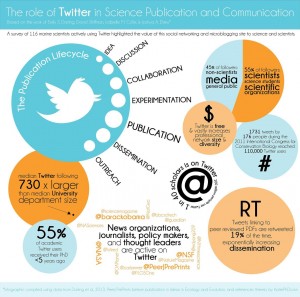 I even started to develop discussions around the US Embassy in Beijing twitter feed in my Atmospheric Chemistry class this past Spring semester, drawing comparisons between my published research from Africa (of essentially PM2.5) and the measurements reported @BeijingAir. I haven’t read my course reviews yet, so I don’t know whether my students liked these discussions or the problem sets that I made related to twitter. I liked it though because it was current and relevant in questions of applied atmospheric chemistry and thinking about our global society. The problems in our backyard are relevant, but I love to think that we as a global civilization can solve problems in a collective way. This philosophy is a natural fit with the concept of social media, and my opinion is that twitter is a better fit than other social media.
I even started to develop discussions around the US Embassy in Beijing twitter feed in my Atmospheric Chemistry class this past Spring semester, drawing comparisons between my published research from Africa (of essentially PM2.5) and the measurements reported @BeijingAir. I haven’t read my course reviews yet, so I don’t know whether my students liked these discussions or the problem sets that I made related to twitter. I liked it though because it was current and relevant in questions of applied atmospheric chemistry and thinking about our global society. The problems in our backyard are relevant, but I love to think that we as a global civilization can solve problems in a collective way. This philosophy is a natural fit with the concept of social media, and my opinion is that twitter is a better fit than other social media.
Then while I’m flipping through one of my various science digest emails over lunch one day, I see this article and realize that there is apparently a collective move of scientists to employing twitter as a serious way to connect. The figure above was posted in that article and you can click and see the higher resolution version. The analysis in that post resonates with how I’m thinking about twitter – namely it allows the science I do to have the potential to be much more relevant. Given that many undergraduates leave the university without even knowing what it is that an “assistant professor” does or what the difference is between an “assistant” and “associate” professor (or that the difference exists), I would say it is critical that the academy makes sure that the future minds walk away from their college degrees with some idea of what it is the professionals in front of the classroom or giving seminars are doing. Most of us assistant professors, for example, are not sitting around after classes stop for the summer drinking margeritas, but in all this surveying of people about climate change and global warming, I haven’t seen questions probing this awareness of what the academy is. Thin Ice actually touches on this topic in terms of what it is an Earth scientist does and why.
Which brings me back to twitter. The graphic above has the key points that I will watch for in twitter: 1. 45% of followers are non-scientists, media, general public, and 2. median twitter following is 730 times median department size. The other points are pretty darn good too! If you want to see what I’m tweeting, thinking, following, etc., visit my twitter feed @brianmagi. I’ll continue to sort through ideas and thoughts and announcements on my personal webpage and blog, but twitter will be great during the academic year when teaching takes a big chunk of my time.