Research
The contribution of the immune system to homeostatic brain function is a growing field that is still not well understood; however, neuroinflammation is increasingly associated with neurocognitive disorders including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and post-infectious West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis, illustrating a need for better understanding of these interactions. Research in the Funk lab investigates the neuroimmune responses to viral infections and their impact on cognitive recovery. Cognitive dysfunction is a well-documented correlate of viral encephalitis; however the underlying molecular mechanisms are unclear. To study the mechanisms of recovery from viral encephalitis, we use murine models of viral infection, specifically the naturally attenuated Kunjin strain (KUNV) of West Nile virus (WNV) and the murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus (MHV). Our overarching hypothesis is that viral encephalitis incites inflammation that accelerates processes of CNS aging, contributing to the development of AD pathology and neurodegeneration.
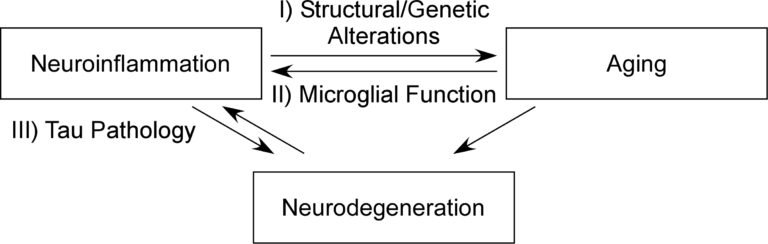
Research in my laboratory uses the viral encephalitis model to investigate I) how neuroinflammation alters genetic and synaptic programs, which affect and denote aging processes, II) how aging affects microglial response to inflammatory events, altering neuroinflammatory signatures, and III) how neuroinflammatory events affect pathological Tau accumulation, a well-studied correlate of neurodegeneration.
Classes Taught
- BIOL 3111 – Cell Biology
- BIOL 4279/5279 – Neurobiology
Education and Training
- 2014-2019 – Postdoctoral research associate with Robyn Klein M.D. Ph.D., Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases
- 2012-2014 – Postdoctoral research associate with Marc Diamond M.D., Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri, Department of Neurology
- 2007-2012 – Ph.D. in Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology with Jeff Kuret Ph.D., Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry
- 2004-2007 – B.A. in Zoology, Miami University, Oxford, Ohio
Current Research Support
RF1 AG084104, PI: Funk 9/1/2023-8/31/2028, Investigating the interactions between viral infection, Tau pathology, and neuroinflammation
Select Publications:
- Reagin KL, Lee R, Williams LA, Cocciolone L, and Funk KE. Compromised CD8+ T cell immunity in the aged brain increases severity of neurotropic coronavirus infection and post-infectious cognitive impairment. Aging Cell. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.14409
- Reagin KL and Funk KE. The Role of Antiviral CD8+ T cells in Cognitive Impairment.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022; 76:102603. PMID 35810534
- Lotz SK, Blackhurst BM, Reagin KL, and Funk KE. Microbial infections are a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021; 15:691136. PMID: 34305533
- Funk KE*, Arutyunov AD*, Desai P, White JP, Soung AL, Rosen SF, Diamond MS, Klein RS. Decreased antiviral immune response within the central nervous system of aged mice is associated with increased lethality of West Nile virus encephalitis. Aging Cell. 2021 Aug;20(8):e13412. PMID: 34327802 *These authors contributed equally to this work
- Funk KE and Klein RS. CSFR1 antagonism limits local restimulation of antiviral CD8+ T cells during viral encephalitis. J Neuroinflammation. 2019; 16:22
- Vasek MJ, Garber C, Dorsey D, Durrant DM, Bollman B, Soung A, Yu J, Perez-Torres C, Frouin A, Wilton DK, Funk K, DeMasters BK, Jiang X, Bowen JR, Mennerick S, Robinson JK, Garbow JR, Tyler KL, Suthar MS, Schmidt RE, Stevens B, Klein RS. A complement-microglial axis drives synapse loss during virus-induced memory impairment. Nature. 2016 Jun 23; 534 (7608): 538-43. PMID: 27337340.
- Funk KE, Mirbaha H, Jiang H, Holtzman DM, Diamond MI. Distinct therapeutic mechanisms of Tau antibodies: promoting microglial clearance vs. blocking neuronal uptake. J Biol Chem 2015; 290(35): 21652-62. PMID: 26126828
- Funk KE*, Thomas SN*, Schafer KN, Cooper GL, Liao Z, Clark DJ, Yang AJ, Kuret J. Lysine methylation is an endogenous post-translational modification of tau protein in human brain and a modulator of aggregation propensity. Biochem J 2014; 462(1): 77-88. PMID: 24869773 *These authors contributed equally to this work
- Thomas SN*, Funk KE*, Wan Y, Liao Z, Davies P, Kuret J, Yang AJ. Dual modification of Alzheimer’s disease PHF-tau protein by lysine methylation and ubiquitylation: a mass spectrometry approach. Acta Neuropathol 2012; 123(1):105-117. PMID: 22033876 *These authors contributed equally to this work
Click Here for Complete List of Published Work in My Bibliography: